So what is hyperpigmentation exactly? You might know hyperpigmentation as dark spots, age spots, sun spots, acne scarring, pregnancy ‘stash, and melasma. Today, I’m going to explain to you each of the different types of hyperpigmentation how to get rid of it.

Hyperpigmentation is really an umbrella term for the discoloration of the skin. Most of the time it is caused by excess exposure to the sun and the harmful UV rays causing an overproduction of melanin which gives our skin that dark spot. But it can also be caused by injury to the skin such as acne or a cut where it has become inflamed resulting in the skin trying to help treat the wound causing discoloration.
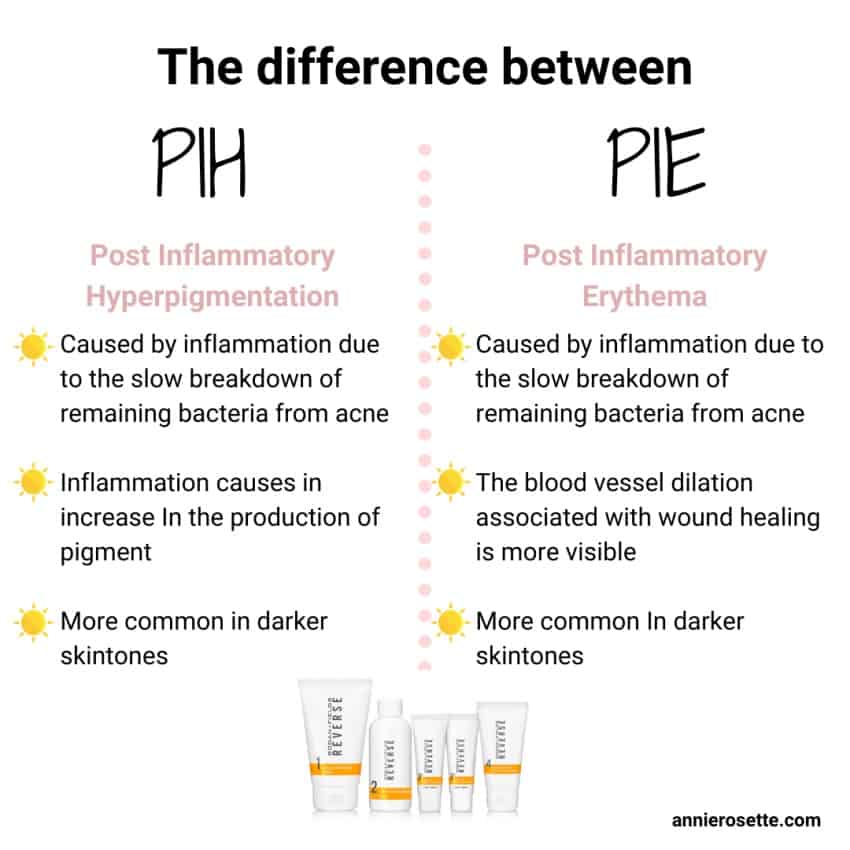
Post-Inflammatory Erythema (PIE) VS Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIE spots are the more reddish, pink marks on your skin usually from post-acne, a cut, and sometimes aggressive exfoliation (no nut scrubs!) This type of Post Inflammatory is more common in lighter skin tones. When the skin is injured, blood rushes to that area to help try to treat it. The blood ends up staying for a while resulting in the red color. This is a vascular and capillary issue as opposed to an overproduction of melanin.
The more inflamed, the worse it gets and the longer it takes to get rid of the spot. You can determine if the spot is PIE by pressing on it and if the color goes away for a second, it’s PIE. it can go away on its own, but you’re looking at 3 months to a year.
PIE and PIH are very similar, however, PIH leaves purple, red, or brown marks and is more common in darker skin tones. The cause is post-acne, a cut or aggressive exfoliation, but the inflammation causes an excess melanin production causing the darker color.
To Avoid PIE/PIH type of hyperpigmentation
- Don’t pick or scratch your face, this will cause more inflammation on zits, rashes, and bug bites
- Don’t ever cleanse, use something gentle to avoid irritating it more. Don’t use brushes on your inflamed areas
- Avoid harsh physical exfoliants
- Don’t put lemon or essential oils on the areas at high concentration.
- Avoid DIY face treatments – Get products designed for your face by dermatologists so the ingredients are in the right dosage
And Then There is Melasma
Melasma shows up in large, splotchy, and spread out found on the cheeks, bridge of nose, forehead, chin, and upper lip. It also is commonly found on the body that is exposed to the sun such as the chest and hands. They are grey-brown or brown in color. It’s caused by genetics, UV exposure, and hormonal influences and is more common in women than in men. It’s also known as a “pregnancy mask”. Melasma is usually more difficult to treat due to the genetic factors that can cause it.

Hyperpigmentation How To Get Rid of It
The skin naturally “sheds” every 28-30 days called the skin cycle to reveal new, fresh skin, but the deeper the ‘wound’ the harder it is to treat especially naturally through the skin cycle.
For products, you need to inhibit melanin production with lightening and brightening ingredients.
For PI’s, you should avoid drying alcohol, not all alcohols are created equal, as well as avoid astringents that strip the skin. (Don’t use witch hazel, it can be too harsh.)
Stop using highly concentrated citrus, tea tree, and other essential oils as they can be very irritating to the skin even for all skin types.
Ingredients to Look for in Products
Acids work for mild hyperpigmentation for lighter skin tones. Look for 10% in these acids for an over-the-counter product. Anything higher will be used by medical professionals in an office.
Retinoids (derived from Vitamin A) alongside an acid to help lighten your hyperpigmentation is a good step if you have darker, more stubborn dark spots. However, don’t use an acid and a retinoid on the same day as they are both harsh and cause irritated skin and disrupt your skin barrier.
- Hydroquinone – decreases melanin production and is the gold standard of hyperpigmentation
- Should NOT use long term
- Should NOT use if you are pregnant
- Works really well when paired with a retinoid
- You have to use it consistently to see results
- Arbutin – inhibits melanin production
- Safe for pregnant women
- Kojic Acid – natural hydroquinone – inhibits melanin production & has lightening effects
- Anti-aging, anti-inflammatory
- Also known as “fermented soy extract” or “fermented rice extract”
- You can use long term
- Need to use with SPF
- Azelaic Acid – best to heal PIE
- Natural
- Helps with inflammation
- AHA – natural from plants & fruits
- Chemical exfoliant
- Licorice Extract – hinders melanin production
- Fights free radicals soothe inflamed skin and regulate oil production
- Zinc Oxide
- Mineral sunscreen
- Vitamin A & C
- Vitamin A – helps with evening the skin tone and texture as well as anti-aging
- Vitamin C – inhibits melanin production and lightens skin
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids that remove the top layer of skin to get rid of hyperpigmentation. There are some at-home options. However, if you go into your dermatologist’s office, they have treatments that are much more powerful and effective.
With chemical peels, you have to avoid the sun like the plague because your skin is so sensitive that you are prone to more hyperpigmentation.
I’m actually using this glycolic acid peel from Exuviance. It can be used twice a week but I am using for my pores and anti-aging.
Laser Treatments
Laser treatments/peels use light beams to lighten the hyperpigmentation.
There are ablative and non-ablative types of lasers.
Ablative lasers are pretty intense and strong and remove layers of your skin.
Non-ablative lasers promote collagen growth and tighten the skin.
Lasers are tricky as they can darken the skin instead of lightening it. Your derm will be able to help determine which route to go.